Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Google’s Use of AI in Search Rankings
- Search Generative Experience
- Optimizing Content for SGE and Large Language Models
- Optimizing for Voice Search
- Using AI to Create Search-Optimized Content
- Content Research & Planning
- Content Publishing
- Limitations of AI for Content Creation
- Google’s Stance on AI-Generated Content
- The Final Verdict: How will AI affect SEO?
- Citations
Introduction
ChatGPT was launched rather unceremoniously to the public just 11 months ago. It has since gone on to become the fastest app to reach 100 million users. Both the large language model (LLM) powering ChatGPT (currently GPT-4) and the application itself have gone through several significant upgrades. ChatGPT has gone on to pass difficult medical, science, law, and business exams[1]; performs tasks using third-party tools; and can now see, hear and speak[2]. With ChatGPT setting new standards in AI capabilities, I’ve found it invaluable in my role as an SEO strategist. This article aims to clarify the role of AI in SEO and provide actionable methods for future-proofing your approach.
Google’s Use of AI in Search Rankings
Google has been using artificial intelligence to understand the meaning of search queries for many years. Its ability to help interpret complex or ambiguous queries helps Google return the most relevant results for each query. Three specific AI technologies used by Google’s search ranking algorithm are RankBrain, Neural Matching, and BERT[2]. These technologies are used to understand the meaning of search queries, assess the quality of web pages, and rank search results more accurately. The detection of spam and other malicious content is also facilitated by AI as Google attempts to protect its users. The consistent rationale for these advancements is the desire to provide searchers with relevant, high-quality search results.
Search Generative Experience
Google’s Search Generative Experience (SGE) began rolling out in May but is not yet available to all users. Google describes SGE as a new way of interacting with search engines that uses AI to generate more comprehensive and informative answers to search queries[3]. If you have access to SGE (you can opt in here), you will see a mixed-media box like the gray one below for some queries.
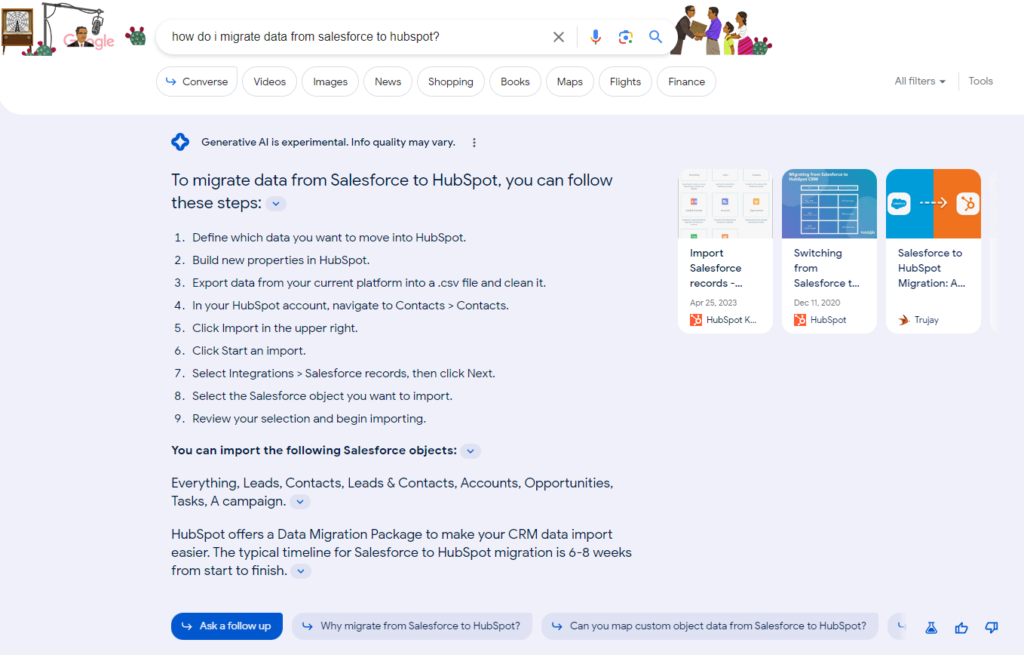
Search Generative Experiences provide comprehensive and highly personalized results through a mixed media format (text, image, code, and video) to provide the best user experience. This new experience continues to evolve but seeks to decrease research time and reduce the number of results that need to be clicked to find answers. Aside from SGE, both Bing Chat and Google Bard already deliver AI-generated results to queries and are reshaping how we seek and retrieve information. These changes in our search habits and expectations will undoubtedly impact how search engines index information, retrieve and prioritize the results.
Optimizing Content for SGE and Large Language Models
In light of the capabilities of SGE and LLMs like those used by ChatGPT, the question becomes: How do we optimize our web content for this new digital frontier? Here are actionable steps to begin future-proofing your search visibility:
- Prioritize quality over quantity: Craft engaging, human-centered content.
- Structure your content logically: Use a hierarchy with clear headings for easy navigation.
- Use natural language: Limit industry jargon for broader readability.
- Include rich media: Incorporate images, videos, audio and code snippets when applicable.
- Use structured data: Use schema to mark up content for search engine and LLM comprehension.
- Strive for speed and compatibility: Ensure that your content loads quickly and functions well on mobile devices.
Though the technologies are still emerging, the core goal of delivering relevant, high-quality results remains the same. Whether your focus is increasing visibility for your brand on Google, Bing, YouTube, or Amazon, always aim to elevate the user experience rather than game the algorithms.
Optimizing for Voice Search
When creating content for the future web, voice search is likely to play a greater role. OpenAI released a multimodal version of ChatGPT, GPT Vision, which can now see speak and hear[4]. GPTV is just starting to role out to a limited group of beta testers but it should begin rolling out to the general public over the next few months. Some of the early use cases are astonishing and far beyond the abilities of SIRI, Alexa and the Google Assistant. It seems probable that we will begin interacting with LLM applications using voice more frequently than we do now. Content can be optimized for voice by targeting more long-tail keywords (ex. “enterprise sales and marketing automation software” vs “marketing automation software”).
Brick and mortar businesses in general already see a high percentage of search traffic coming from mobile devices and voice search. This trend could accelerate with multimodal search and chat applications. Claiming and optimizing your Google Business profile and getting listed in relevant local directories will continue to be important when optimizing for voice search.
Using a variety of specialized tools and tactics empowers you to use this technology to augment your processes – achieving better results in a shorter period of time.
Using AI to Create Search-Optimized Content
Until now we’ve looked at how AI will impact the search experience. But AI will arguably have an even greater impact on the creation of content surfaced by these models. Literally thousands of AI tools have sprung up over the past year that empower creators to plan, create, optimize, analyze and promote content faster, cheaper and more effectively than ever before.
Content Research & Planning
LLM-based chat applications like ChatGPT, Bard, Bing Chat and Claude 2 can be used to brainstorm ideas and flesh out content outlines. The quality of responses received from these tools is very much dependent on the quality of the prompts used. Taking the time to learn some basic prompt engineering techniques like few-shot prompting, the “Persona Pattern”, and the “Cognitive Verifier Pattern”[5] will empower you to create unique content that stands out from the competition. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each application will also help you research and plan content that is structured the way you want it.

Original content has a greater chance of ranking in the search results. So too does content that includes semantically related words and links to authoritative data sources. Generative AI tools can be used for keyword research and to identify relevant and authoritative citation sources. Today’s chat models can be prompted to brainstorm keywords, propose topics based on those keywords, identify current content gaps and create content outlines addressing those gaps.
Content Publishing
In addition to researching and planning content, AI-powered tools can be used to create engaging, search-optimized titles and meta descriptions, and even captions for your images. Tools like ChatGPT are also adept at fixing spelling and grammar, changing perspective and altering the tone of your work to align more closely with your brand and/or your audience. You can certainly skip all these individual steps and have an article, landing page or other piece of content written for you with a single prompt. However, the results from this approach are often uninspiring with mediocre content that does not align with your brand or provide any real insight for your readers.
Limitations of AI for Content Creation
Despite the impressive capabilities already demonstrated by the early era of generative AI, it is not without many limitations. When it comes to content creation, many organizations and individuals are reluctant to adopt tools like ChatGPT due to one or more of the following:
- Lack of creativity: Large language models excel at generating content similar to what they’ve been trained on. Although prone to creating content that lacks creativity, models can be prompted (or coaxed) to exercise more creativity by using methods such as Chain-of-Thought prompting[6].
- Inaccuracy: LLMs like ChatGPT often hallucinate. They confidently spew information that is inaccurate or factually incorrect. Depending on the task, the generation of inaccurate responses can sometimes be mitigated with prompt engineering methods like Self Reflection[7]. It is still essential to always fact check the output from these applications – including the accuracy of their citations. Learning about the accessible memory of your application, referred to as the context window, will help you avoid inaccurate responses arising from long chat sessions or working with large amounts of text.
- Copyright Infringement: Generative AI can be used to create original works of authorship. However, it can also inadvertently generate text that is similar or identical to copyrighted text that results in plagiarism. Breaking down the content creation process into several steps can decrease the odds of this occurring. Plagiarism detection tools like Copyscape can be used as a safeguard before publishing AI-assisted content.
Even with these limitations, generative AI can make content creation significantly more productive. Web content produced with the assistance of AI has the potential to outrank human-written content when it adheres to Google’s recommended quality guidelines.
Google’s Stance on AI-Generated Content
Google has historically penalized websites that used mass methods of content generation. Their spam policies state that using automation (including AI) to manipulate rankings is prohibited. These policies have recently been updated with specific guidance about AI-generated content. They reiterate that content created should demonstrate the qualities of E-E-A-T (experience, expertise, authoritativeness and trustworthiness)[8]. They also state that their focus is “on the quality of content, rather than how the content is produced”. If you are using AI to help create better content, you have the potential to be rewarded with increased search visibility. If you are using it to mass publish low-quality articles, you risk degrading your brand and incurring algorithmic search penalties. Look no further than the backlash experienced by prominent brands like Buzzfeed and CNET to see the consequences of this ill-conceived practice.
The Final Verdict: How will AI affect SEO?
The way we search and retrieve information is undergoing a transformative shift. The multibillion-dollar AI arms race between Google, Microsoft and other players signals a major upending of the status quo when it comes to organic search. While there is a learning process required to adapt to these changes, those who act early are poised to reap the benefits. AI can be used to quicken content production and improve its performance when used to its potential. Creating exceptional human-centered content for your audience and making it easier for search engines and large language models to understand your content are the core components of an SEO strategy that will stand the test of time.
Citations
- Varanasi, Lakshmi. “AI models like ChatGPT and GPT-4 are acing everything from the bar exam to AP Biology. Here’s a list of difficult exams both AI versions have passed.” Business Insider, 25 Jun. 2023, https://www.businessinsider.com/list-here-are-the-exams-chatgpt-has-passed-so-far-2023-1.
- Schwartz, Barry. “How Google Uses Artificial Intelligence In Google Search.” Search Engine Land, 3 Feb. 2022, https://searchengineland.com/how-google-uses-artificial-intelligence-in-google-search-379746.
- “Learn as You Search (and Browse) Using Generative AI.” Google, https://blog.google/products/search/google-search-generative-ai-learning-features/.
- OpenAI. “ChatGPT Can Now See, Hear, and Speak.” OpenAI Blog, 25 Sep. 2023, https://openai.com/blog/chatgpt-can-now-see-hear-and-speak.
- White, Jules, et al. “A Prompt Pattern Catalog to Enhance Prompt Engineering with ChatGPT.” ArXiv, https://arxiv.org/pdf/2302.11382.pdf.
- Wei, Jason, et al. “Chain-of-Thought Prompting Elicits Reasoning in Large Language Models.” ArXiv, https://arxiv.org/pdf/2201.11903.pdf.
- Shinn, Noah, et al. “Reflexion: An Autonomous Agent with Dynamic Memory and Self-Reflection.” ArXiv, https://arxiv.org/pdf/2303.11366.pdf.
- “Google Search’s Guidance About AI-Generated Content.” Google Search Central Blog, Feb. 2023, https://developers.google.com/search/blog/2023/02/google-search-and-ai-content.



